Indoor air quality affects our health and well-being more than we realize. At Cleaning Rabbit, we understand the importance of breathing clean air in our homes and workplaces.
This guide will show you how to effectively monitor indoor air quality, from understanding common pollutants to using the right tools for assessment. We’ll also cover how to interpret air quality data and take action, including tips on HVAC vent cleaning to improve overall air quality.
What Is Indoor Air Quality?
Definition of Indoor Air Quality
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) refers to the air quality within and around buildings and structures, particularly as it relates to the health and comfort of building occupants. We at Cleaning Rabbit understand the profound impact IAQ can have on people’s well-being.
Common Indoor Air Pollutants
Several pollutants can compromise your indoor air quality:
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): These tiny particles originate from various sources, including dust, pollen, and smoke.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Many household products emit VOCs, including paints, cleaning supplies, and even some furnishings.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): While not typically harmful in normal concentrations, high levels can indicate poor ventilation.
- Mold and Mildew: These fungi thrive in damp environments and release spores into the air.
- Radon: This colorless, odorless gas is the number one cause of lung cancer among non-smokers and the second leading cause of lung cancer overall in the United States.
Health Impacts of Poor IAQ
Poor indoor air quality can lead to both short-term and long-term health effects.
Short-term effects include:
- Irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
Long-term exposure to poor IAQ can result in more serious conditions:
- Respiratory diseases
- Heart disease
- Cancer
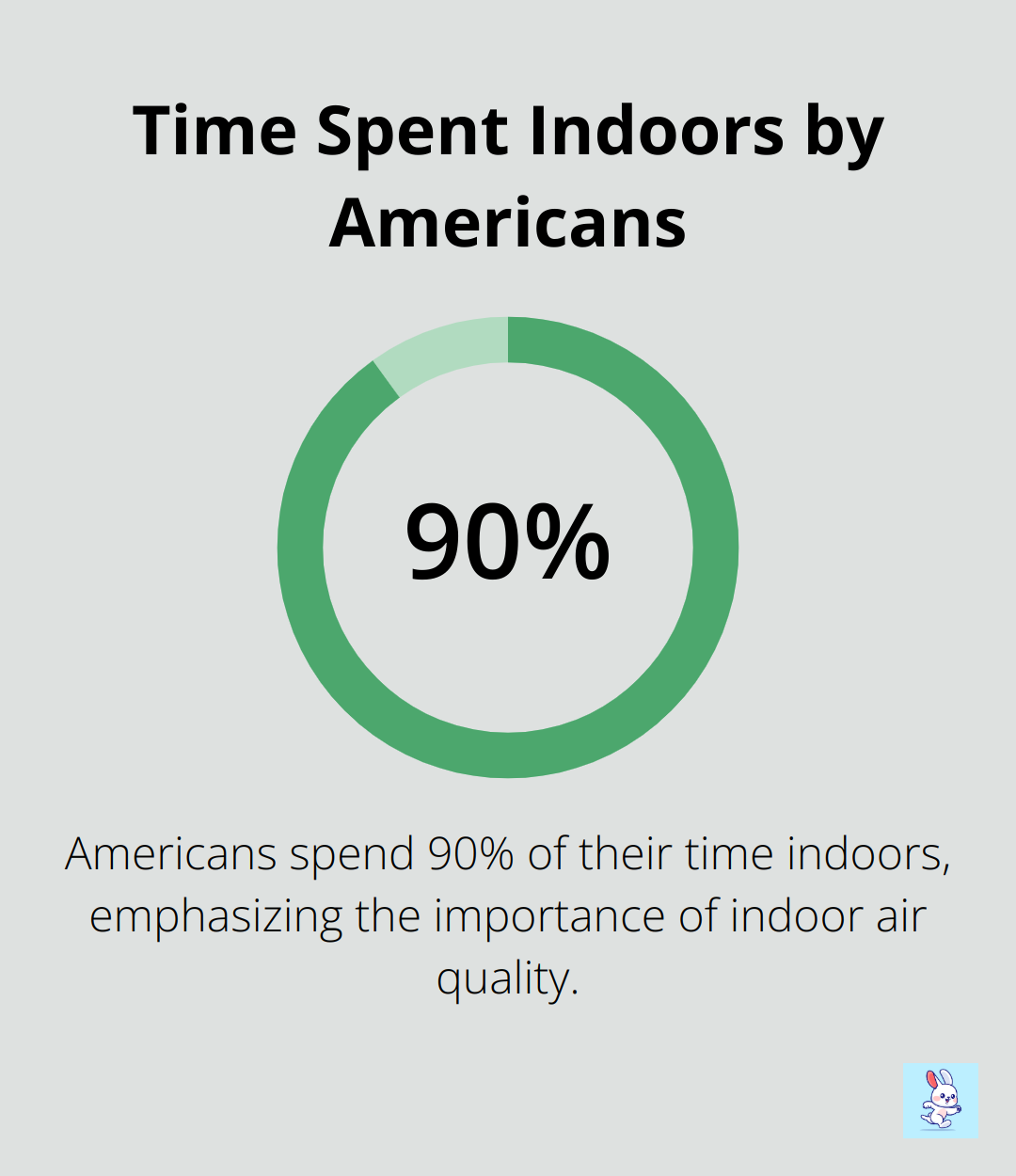
The EPA reports that indoor air can be two to five times more polluted than outdoor air. This statistic highlights the importance of monitoring and improving your indoor air quality, especially considering that Americans, on average, spend approximately 90 percent of their time indoors.
Importance of IAQ Monitoring
To effectively monitor your indoor air quality, you need the right tools. Air quality monitors can measure various pollutants, including particulate matter, VOCs, and CO2. Some advanced models even track humidity and temperature, which can affect the growth of mold and mildew.
Regular HVAC maintenance (including air duct cleaning) is essential for maintaining good IAQ. Professional cleaning services use HEPA-filtered equipment to thoroughly clean air ducts, removing accumulated dust, allergens, and other pollutants that can circulate through your home.
Now that we understand what indoor air quality is and why it matters, let’s explore the tools and methods available for monitoring IAQ effectively.
How to Choose the Right IAQ Monitoring Tools
Air Quality Monitors and Sensors
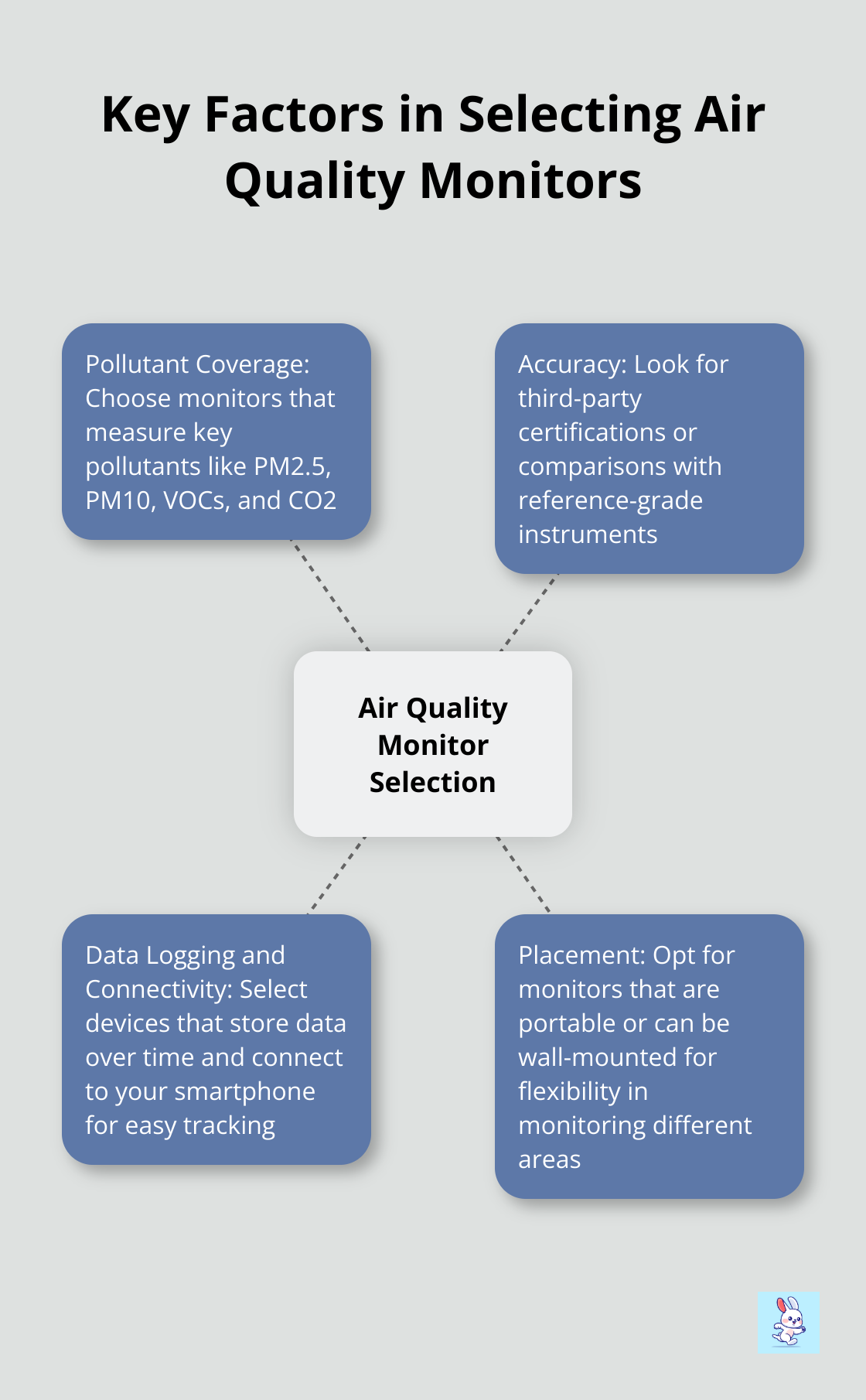
Air quality monitors form the foundation of any IAQ monitoring strategy. These devices measure various pollutants and environmental factors in real-time. When selecting a monitor, consider these factors:
- Pollutant Coverage: Select monitors that measure key pollutants like PM2.5, PM10, VOCs, and CO2. Some advanced models also track temperature and humidity.
- Accuracy: Look for third-party certifications or comparisons with reference-grade instruments.
- Data Logging and Connectivity: Choose devices that store data over time and connect to your smartphone for easy tracking.
- Placement: Opt for monitors that are portable or can be wall-mounted for flexibility in monitoring different areas of your home or office.
The Airthings View Plus offers comprehensive measurements (CO2, PM2.5, VOCs, radon, humidity, temperature, and air pressure). For those focused on CO2 levels, the SAF Aranet 4 CO2 monitor provides accurate readings. However, CleaningRabbit’s professional-grade monitors offer the most reliable and comprehensive measurements for your indoor air quality needs.
DIY Testing Kits
While not as thorough as continuous monitors, DIY testing kits can provide valuable insights into specific pollutants:
- Radon Test Kits: These kits detect this odorless, cancer-causing gas. Short-term kits provide results in 2-7 days, while long-term kits offer a more accurate assessment over 90+ days.
- Mold Test Kits: These help identify the presence of mold spores in your air. (Professional testing is recommended for accurate results and identification of mold species.)
- VOC Test Kits: These use color-changing badges to indicate the presence of VOCs. They offer a quick assessment but don’t provide detailed concentration levels.
DIY kits offer a snapshot of air quality at a specific time and may not capture fluctuations throughout the day or week.
Professional Air Quality Assessments
For the most comprehensive and accurate evaluation of your indoor air quality, professional assessments stand out. These assessments typically include:
- Visual Inspection: Professionals examine your home for visible signs of mold, water damage, or other potential IAQ issues.
- Advanced Testing Equipment: They use calibrated, professional-grade equipment to measure a wide range of pollutants accurately.
- HVAC System Evaluation: This includes checks for proper ventilation, filter efficiency, and potential contaminants in your ductwork.
- Detailed Report and Recommendations: You’ll receive a comprehensive analysis of your IAQ and specific steps for improvement.
Professional air quality assessments provide practical suggestions on preventing, identifying, and resolving indoor air quality problems in public and commercial buildings. The next step after choosing your monitoring tools is to understand how to interpret the data they provide, which we’ll explore in the following section.
How to Read Air Quality Data
Understanding Key Air Quality Metrics
Air quality monitors measure several important pollutants. Particulate matter (PM) is quantified in micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m³). The EPA classifies PM2.5 levels under 12 µg/m³ as good, while levels above 35 µg/m³ are unhealthy. For volatile organic compounds (VOCs), readings below 0.3 mg/m³ indicate low levels, while readings above 0.5 mg/m³ are high and may require action.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) levels are measured in parts per million (ppm). CO2 levels indoors should be as close to 400 ppm (outdoor CO2 concentration) as possible, and no more than 1000 ppm above outdoor air. Levels above 1,000 ppm suggest poor ventilation and can cause drowsiness or headaches.
Identifying Dangerous Pollutant Levels
When you analyze your air quality data, watch for sudden spikes or consistently high readings. If your PM2.5 levels frequently exceed 35 µg/m³, investigate potential sources such as nearby construction, heavy traffic, or indoor smoking.
VOC levels often increase after painting, using cleaning products, or introducing new furniture. Sources of VOCs include paints, paint strippers and other solvents, wood preservatives, aerosol sprays, cleansers and disinfectants, and moth repellents. If levels remain high for extended periods, try to increase ventilation or use air purifiers with activated carbon filters.

For CO2, levels consistently above 1,000 ppm indicate inadequate ventilation. This often occurs in bedrooms overnight or in crowded, poorly ventilated spaces. Opening windows or adjusting your HVAC system can help lower these levels.
Recognizing IAQ Trends Over Time
Long-term data analysis reveals patterns that single readings might miss. You might notice that PM2.5 levels rise every morning around rush hour if you live near a busy road. This insight could prompt you to keep windows closed during these times or invest in better air filtration.
Seasonal trends also play a role. Many homes experience higher VOC levels in summer due to increased off-gassing from materials in warmer temperatures. Winter often brings higher CO2 levels as people keep windows closed to conserve heat.
Taking Action Based on Air Quality Data
Understanding these patterns allows you to take proactive steps to maintain good air quality year-round. If you notice consistently high PM levels, consider professional air duct cleaning services (CleaningRabbit offers top-notch services in this area). Regular cleaning can significantly reduce particulate matter and improve overall air quality.
For high VOC levels, identify and remove potential sources (e.g., certain cleaning products or new furniture). Increase ventilation and use air purifiers with activated carbon filters to absorb these compounds.
To address elevated CO2 levels, improve ventilation by opening windows when possible or using mechanical ventilation systems. In office environments, consider adjusting occupancy levels or increasing fresh air intake in HVAC systems.
Final Thoughts
Monitoring indoor air quality empowers you to protect your health and well-being. You can take control of your indoor environment when you understand common pollutants, use appropriate monitoring tools, and interpret air quality data effectively. Regular air quality checks provide valuable insights into the air you breathe daily, which allows you to identify potential issues before they become serious health concerns.
You must act on the data you collect to maintain optimal indoor air quality. This may involve simple steps like increasing ventilation, using air purifiers, or removing sources of pollutants. For more comprehensive solutions, you should consider professional services such as HVAC vent cleaning, which can significantly reduce particulate matter and improve overall air quality.
CleaningRabbit specializes in residential and commercial air duct cleaning, dryer vent cleaning, and HVAC sanitation. We use advanced HEPA-filtered equipment to clean your indoor environment. You can create a healthier, more comfortable living or working space when you combine regular monitoring with professional cleaning services.

